LLOR: LLVM OpenMP Repairer
Introduction
Parallelism has become a cornerstone for achieving high-performance computing. However, parallelism has its challenges, and one such challenge is nondeterminism. Nondeterminism in programs is a behavior where the program produces different outputs for the same input. There could be several causes for nondeterminism in programs. In parallel programs, one of the sources of nondeterminism is schedule nondeterminism, which may cause data race errors. Identifying the root cause and fixing these errors is nontrivial.
LLOR is a tool that attempts to address this by implementing a language-independent approach to provide appropriate placements of synchronization constructs to avoid data races. LLOR can fix data race errors in C/C++ and Fortran programs that use the OpenMP API. It can also remove barriers that are deemed unnecessary for correctness.
LLOR targets two OpenMP pragmas: omp parallel regions and omp parallel for loops.
Architecture
The implementation of LLOR leverages LLOV, a state-of-the-art data race checker. LLOV identifies data races in C/C++ and Fortran programs. It is built as an analysis pass using the LLVM compiler infrastructure. The architecture of LLOR consists of two components: Instrumentation and Repair. The architecture of LLOR is depicted in the below figure:
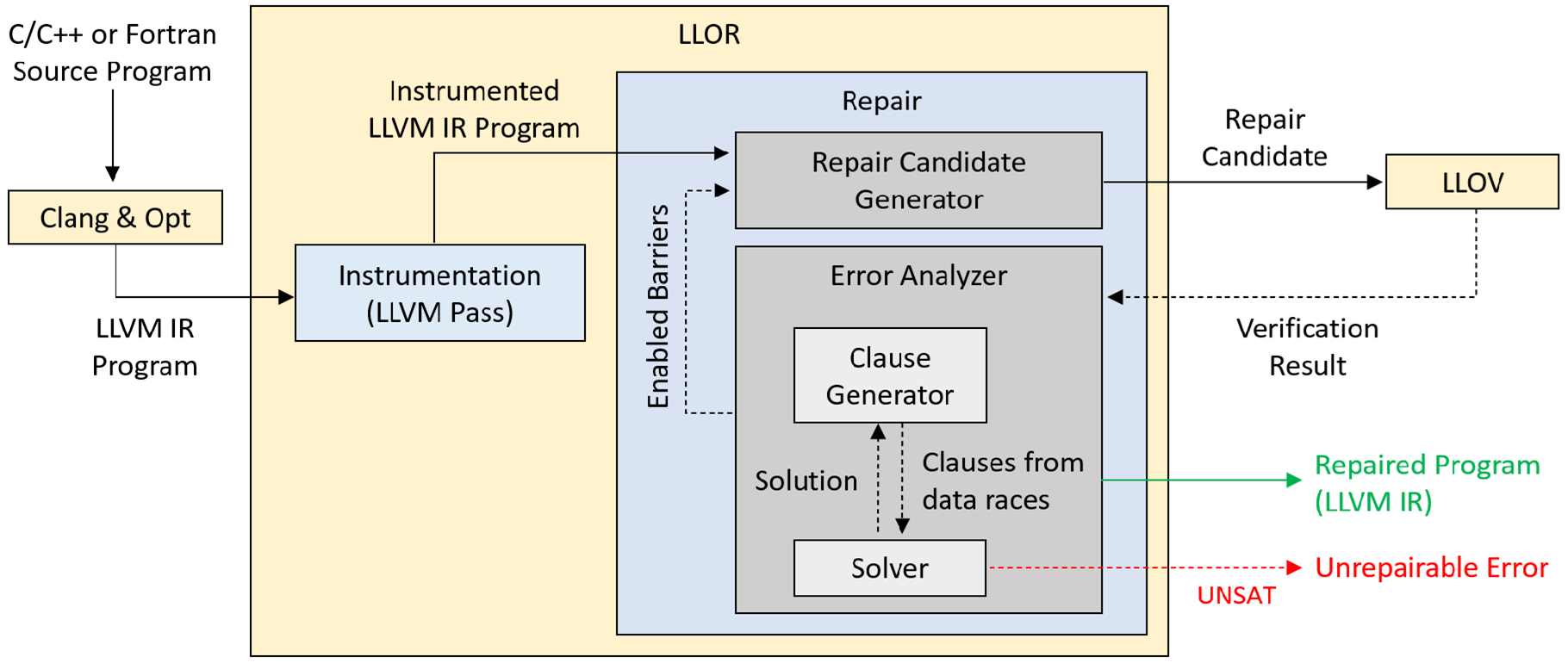
The instrumentation component adds metadata that indicates the possible locations of barriers in the case of parallel regions. In the case of parallel for loops, this metadata marks the possible statements that have to be a part of an ordered region.
The repair component takes an iterative approach. In each iteration, LLOV is called with a repair candidate to check if the program is error-free. If LLOV identifies any data races, constraints are generated from these errors to avoid them in subsequent iterations. The Solver is called with these constraints to obtain a solution that determines which synchronization constructs have to be enabled or disabled while generating the next repair candidate.
Experiments
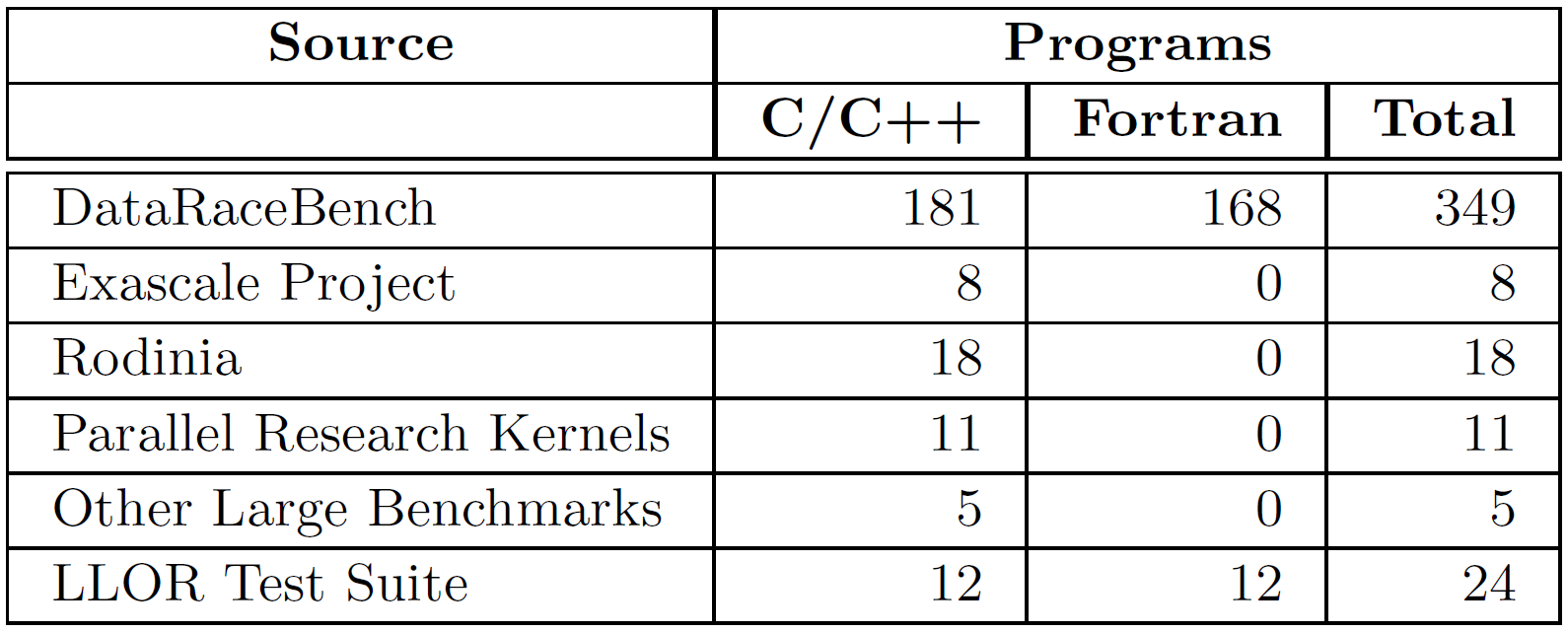
A total of 415 programs (235 C/C++ and 180 Fortran) were considered for evaluating LLOR. This benchmark set consists of programs from the DataRaceBench test suite, Exascale project, Rodinia test suite, and Parallel Research Kernels, along with additional benchmarks introduced while developing LLOR. The table below summarizes the distribution of the benchmark set.
The results obtained from running LLOR against the benchmark suite are summarized in the table below. The table categorizes the results into three categories based on the output of LLOV. The first category includes all the programs for which LLOV concluded that there were no errors. LLOR suggests removing unnecessary barriers and ordered regions if they are not needed for correctness.
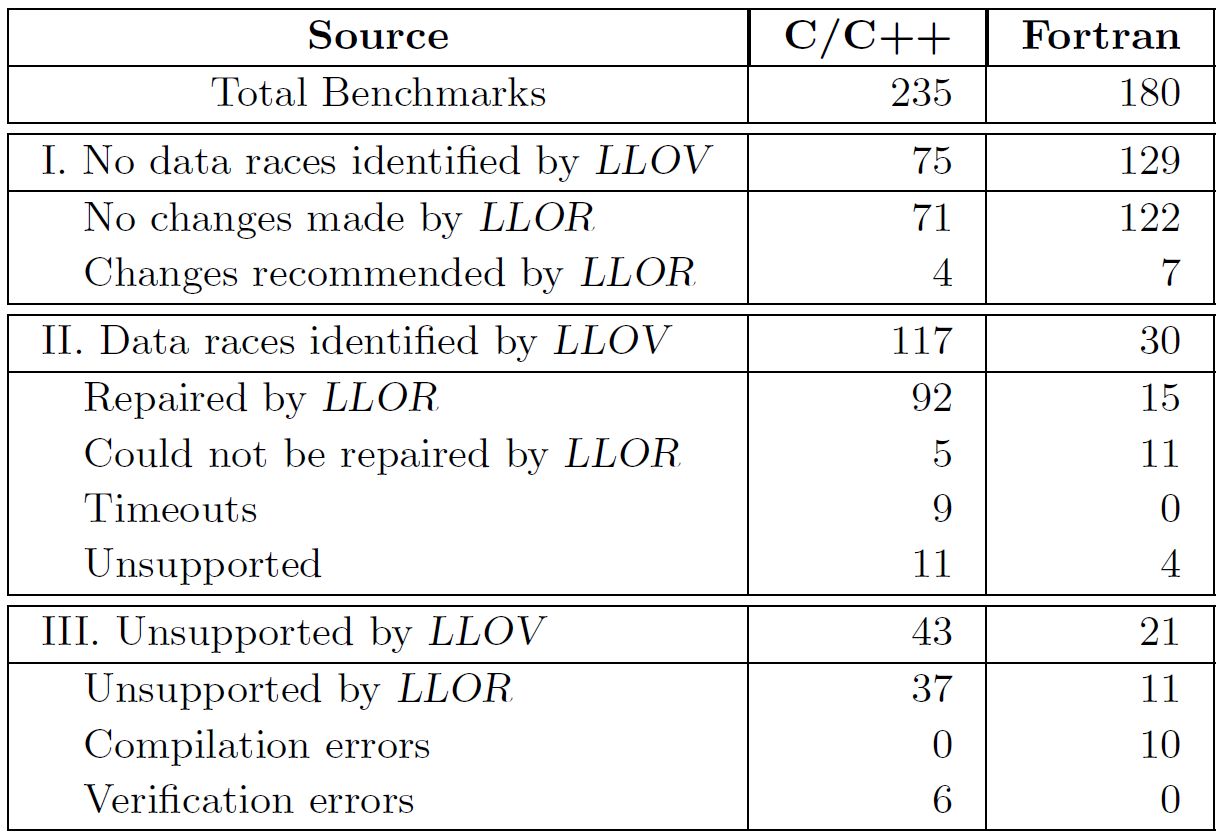
The second category includes the programs for which LLOV had identified data races. Out of the 147 programs in this category, LLOR was able to fix 107 programs correctly. LLOR was unable to repair 16 programs since it could not find any assignment that satisfied the clauses generated during the repair phase. The final category includes the programs that are either unsupported by LLOV or failed compilation. There are 64 programs in this category.
These experimental results can be reproduced using the pre-built binaries available at https://zenodo.org/records/13938526. This artifact has been evaluated by the VMCAI’25 artifact evaluation committee.
The source code of LLOR and a developer guide are available at https://github.com/cs17resch01003/llor.
Publications
1. LLOR: Automated Repair of OpenMP Programs
Utpal Bora, Saurabh Joshi, Gautam Muduganti, Ramakrishna Upadrasta
Published in VMCAI’25 (pre-print) (Talks: VMCAI’25)
Contact
For any issues, questions, comments or suggestions, feel free to reach out to us at cs17resch01003@iith.ac.in.
Last Modified: January 29, 2026